The glycemic index ranks the effects of carbohydrates on blood glucose levels. Now that may seem a bit confusing, so lets break it down a little easier.
Carbohydrates are the sugars, starches, and fibers found in foods. They provide fuel for the nervous system and energy for working muscles.
Blood glucose levels are just blood sugar levels, which is the amount of sugar in your blood.
The glycemic index ranks how quickly the carbohydrates you eat are broken down into glucose, and released into the bloodstream. Thus increasing your blood sugar levels.
This spike in blood sugar will either require your body to release insulin quickly, or for diabetics, will require a shot of insulin.
In either case this quick spike of insulin will tax your body and increase inflammation. Two things that we want to avoid.
How do you avoid an insulin spike? By choosing low glycemic carbohydrates.
When a carbohydrate breaks down slowly, it slowly releases sugar into your blood. This is called a low glycemic index carbohydrate because you have a slow and steady supply of sugar being released into your blood.
This means you have a slower digestion rate and absorption of starches and sugars.
Some low glycemic foods are peanuts, broccoli, cucumber, peppers, tomatoes, and more.
You can probably guess that carbohydrates with a high glycemic level means the carbohydrates break down rapidly, releasing sugars into the blood quicker.
Some high glycemic roods are white bread, watermelon, waffles, pretzels, candies, and more.
Low glycemic foods are better for you!
High glycemic foods may be very detrimental to your health because it can raise your blood sugar, which pushes your endocrine system. A low glycemic diet has many benefits to your body, such as improving diabetes control, reduce the risk of heart disease, reducing cholesterol levels, prolong physical endurance, and many more.
Should you always avoid high glycemic carbohydrates?
Not necessarily, high glycemic foods still should sometimes be in your diet because they help refuel carbohydrates after exercise.
The Glycemic Index can change.
Just because the food item is given a certain number (low or high) on the glycemic list doesn’t mean it always has the same rating, I know, that sounds confusing right.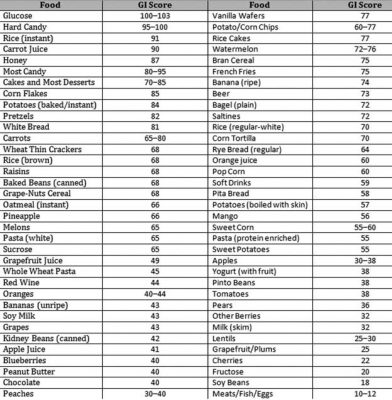
The glycemic Index can change depending on preparation and ripeness. If the food is prepared with fat, fiber, or acid, it could lower the release of carbohydrates into your bloodstream causing it to be low glycemic instead of high.
Fat and fiber especially slow the rate of digestion, thus slowing the release into the body and lowering the glycemic index rating.
On the other hand, the longer you cook starches the higher they will get on the index, as you cook starches, you break them down and convert them into sugar, which is more quickly digested and absorbed.
Another change is in ripeness, fruit and vegetables will increase on the glycemic index the more they ripen. Have you ever eaten an unripe banana? They taste very starchy and dry, as they ripen that starch converts into sugar and increases their rating on the glycemic index.
Don’t overlook the index because it actually helps you.
The glycemic Index does serve a purpose, and in fact people with weight problems, diabetes, and high cholesterol use the index everyday when choosing what to eat.
Many Americans have come to not care about what they eat, as long as they stay in their calorie limit, but those people don’t really understand the way that food works in the body.
If you eat the wrong foods it could affect your health, even if you stay in your calorie limit. The index is here to help you stay healthy so you can look good and feel good.
If you need help understanding the glycemic index please let us know and one of our nutritionists would be happy to help you out. Or you can check out our online services and get all the information you need wherever you are.

